
Cialis ist bekannt für seine lange Wirkdauer von bis zu 36 Stunden. Dadurch unterscheidet es sich deutlich von Viagra. Viele Schweizer vergleichen daher Preise und schauen nach Angeboten unter dem Begriff cialis generika schweiz, da Generika erschwinglicher sind.
March april 2002 nutrinews

8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:43 AM Page 1
Recent health and nutrition information from Douglas Laboratories March/April 2002
NUTRACEUTICAL APPROACHES TO CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
Mitchell J. Ghen, D.O., Ph.D.
Outside of the medical/surgical
neously. It is this concerted effort that
focusing on supplemental issues, there is
model for heart disease, modern practi-
should prove to have maximum impact
a marked importance in appropriate
tioners should consider complementary
on quality and quantity of life issues for
dietary intervention as well.
approaches to assist their patients. The
the coronary artery disease patient.
stand-out difference between the two
Therefore, we will consider the issues of
approaches is that the complementary
inflammation, infection, hormones, lipids,
One of the primary treatments applied
strategy attempts to break the underlying
platelet aggregation, vasodilation,
for patients with coronary artery disease
pathology perpetuating the disease. The
antioxidants, sympathetic tone, stress,
are anticoagulants. The aging process
best example is arteriosclerotic cardio-
insulin resistance and homocysteine. You
lends itself to increased coagulability. The
vascular disease, an epidemic malady of
may note that several nutrients may be
obvious consequence of hypercoagula-
the industrialized nations. With so many
mentioned or noted twice due to their
bility is clot formation and subsequent
products available today, it is best to
multiple types of action. It is best that you
artery occlusion. Increase in blood vis-
approach the discussion by grouping
choose at least one from each of these
cosity can create a hemodymamic state
nutraceuticals by their physiologic
categories, utilize the proper dose, eval-
of ischemia, with its own set of circum-
actions. Our nutritional knowledge base
uate the efficacy and then add or sub-
stances. Ischemia is defined as low blood
continued on page 2
today helps us to recognize key areas of
tract substances depending on your
concern that must be addressed simulta-
patient's response. Though this article is
NSIDE THIS ISSUE
• Nutraceutical Approaches to
Table 1 – Anticoagulant Activity
Coronary Artery Disease
• Anticoagulants . . . . . .page 1
Alpha-tocopherol . . . . . . . . .400-1600 I.U./day
• Vasodilation . . . . . . .page 2
Arginine . . . . . . . . . . . 2000-6000 mg/day
• Lipid Modulation . . . . .page 2
Ascorbic acid . . . . . . . . . .1000-4000 mg/day
• Homocysteine Reduction . . page 3
Bromelain . . . . . . . . . . .500-3000 mg/day
• Antioxidants and
Curcuma longa . . . . . . . . . 200-1200 mg/day
Biological Enzymes . . . . page 5
E.D.T.A.-Oral or rectal suppository . . .Dose varies depending on renal fx
• Inflammation and Infection . page 5
Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) . . . . . 5000-10,000 mg/day
• Sympathetic Tone . . . . .page 6
Ginger (powdered) . . . . . . . .1/2 to 1 tspn/3 times a day
• Ionotropic and Chronotropic
Ginkgo biloba . . . . . . . . . 40-120 mg/day
Augmentation . . . . . .page 6
Inositol hexanicotinate . . . . . . .400-3000 mg/day
• Gamma-Tocopherol . . . . .page 4
Magnesium . . . . . . . . . . 300-1600 mg/dayN-acetyl cysteine . . . . . . . . .500-3000 mg/day
• Coenzyme Q10:
Pancreatin . . . . . . . . . . .300 mg/day
A Brief Description . . . . . page 7

8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:43 AM Page 2
flow, which may or may not have total
Table 2 – Vasodilation
obstruction associated with it. Ischemia can
Arginine . . . . . . .3000-6000 mg/day
lead to apoptosis and inflammation.
Garlic . . . . . . . .400-600 mg/day
Evaluation of ischemic potential can be
Hawthorne . . . . . . 160-250 mg of the flower (standardized)
approached with a functional coagulation
Horse chestnut . . . . . 600-700 mg (standardized to aecins)
panel. This composite of tests includes the
Capsicum (cayenne) . . . 40,000-100,000 heat units 1-6 capsules/day
typical PT, PTT tests and also the more
aspirin still have clot formation. In con-
or by vasospasm. The natural substance,
comprehensive combination of fibrino-
trast EDTA (ethylene diaminetetracetic
arginine, for example, is said to increase
gen, prothrombin fragments one and
acid), inhibits aggregation to all of the
nitric oxide, a free radical (part of a
two, thrombin-anti-thrombin complexes,
substances above with the exception of
group of compounds known as endothe-
soluble fibrin monomers and platelet
collagen. Acute phase reaction, particu-
lial releasing factor, EDRF) that functions
CD62P (Selectin) receptors. A valuable
larly a high c-reactive protein, is related to
as a vasodilator. Nitric oxide has a sec-
test for evaluation of clotting is platelet
vascular inflammation and or infection.
ondary effect to potentially reduce the
aggregation testing. Platelet aggregation
Substances, such as coumadin affect pro-
damage created by homocysteine. It has
occurs with the presence of adenosine,
thrombin/thrombin activation. Natural
been hypothesized that EDTA's benefit
epinephrine, collagen and thrombin.
products like vitamin E and magnesium
can, to a large degree, be attributed to its
Most anti-platelet aggregation medica-
have similar properties. Platelet hyperac-
release of nitric oxide. Of course, EDTA is
tions work only in the presence of adeno-
tivity is minimized by aspirin and similarly
an excellent anti-coagulant.
sine (aspirin for example). This may
by other natural products like ginkgo and
explain why type A personalities using
Also worthy of note, cayenne pepper
ginger. Fibrinogen/fibrin monomers can
has excellent effects on blood lipids,
be addressed with enzymatic therapy like
platelet activity, and vasodilatory action.
bromelain and pancreatin. Natural sub-
As a wonderful first aid remedy, one tea-
stances, that have similar reaction to
spoon of cayenne in a glass of water can
Publisher . Peter W. Hefele
heparin, are arginine, niacin, bromelain
quickly relieve the discomfort of acute
Editor In Chief . Andrew D. Halpner, Ph.D.
and papain. I have found clinically that
chest pain caused by angina.
Assistant Editor . Michael Traficante
increased fibrinogen levels of greater than
Assistant Editor
400 mg respond quickly and effectively to
& Research . Natalie Shamitko
Curcuma longa.
There are many products that effec-
Nita Bishop, Clinical Herbalist
tively control dyslipidemia without the
Martin P. Gallagher, M.S., D.C.
side effects often associated with conven-
An important component to coronary
Mitchell J. Ghen, D.O., Ph.D.
tional medical drugs. For elevated cho-
artery disease treatment is vasodilation.
Brad Lichtenstein, N.D.
lesterol, a combination of pantethine and
Derek DeSilva Jr., M.D.
The consequence of vasodilation is
inositol hexacotinate can demonstrate
James Wilson, Ph.D.
improved blood flow and subsequent
profound improvements in one month.
increase in tissue oxygenation. The
For those patients with elevated triglyc-
object of nitrates or nitrate therapy, a
eride levels, L-Carnitine, as well as EFAs,
Pittsburgh, PA 15205
mainstay of both acute and chronic coro-
can often solve the problem. I prefer the
Phone: (412) 494-0122
nary arterial disease care is to increase
Fax: (412) 278-6804
inositol hexanicotinate form of niacin due
blood flow to constricted blood vessels,
to its absence of the troublesome side
whether this stricture is created by plaque
8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:43 AM Page 3
B6, B12 and folic acid deficiency. Even
Table 3 – Lipid Modulation
Raloxefen's benefit as seen in the Ruth
Pantethine . . . . . . . . . . . . .500-1,000 mg/day
Study "Raloxefen use for heart study"
Inositol hexanicotinate . . . . . . . . 3000 mg/day
suggested this drug's action on coronary
Garlic . . . . . . . . . . . . . .400-600 mg/dayL-Carnitine . . . . . . . . . . . . .1000-3000 mg/day
artery disease, may in part be due to its
Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) . . . . . . .
5000-10,000 mg/day
homocysteine-lowering qualities. Regular
MIC (methionine-inositol choline) . . . . . 200-400 mg/day of each
supplementation with the three B vitamins
Lpa (lipoprotein a) — decreasing agents
(B6, B12 and folate) will control a great
Inositol hexanicotinate . . . . . . . . .
majority of elevated homocysteine levels.
A simple blood test confirming the
Vitamin C . . . . . . . . . . . . .1000-2000 mg/day
patient's level of homocysteine should be
L-Lysine . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1000-2000 mg/day
performed with their annual routine
effects of flush and liver irritation. Its
gation used omega-6 fatty acids as well. In
exam. Although laboratories suggest that
mechanism of action is similar to all
refractory cases of elevated lipids, which
a level below 15 is normal, a level of less
niacin compounds to reduce plasma
have failed to respond to the above regi-
than 10 is ideal and less than 7 is con-
triglycerides, VLDL, LDL synthesis and
men, consider the combination of methion-
sidered optimal.
total cholesterol. Pantethine is the active
ine, inositol and choline in doses of 200-
hormone of pantethenic acid. It is consid-
400 mg of each taken 3 times daily.
Insulin Resistance Reduction
ered to be one of the most important
Lipoprotein a (Lpa) is an apolipoprotein,
Receptor sensitivity for insulin
parts of coenzyme A (CoA) that trans-
i.e. an LDL particle, to which an additional
decreases and the body compensates by
ports fats to and from the cells. It has a
protein is attached. Because of Lpa's simi-
secreting increased amounts of insulin.
potent effect on cholesterol as well as
larity with plasminogen, it interferes with
This is known as ‘insulin resistance'.
triglycerides. L-Carnitine is synthesized
fibrinolysis, and of course ultimately speeds
Increased insulin levels promote lipogen-
from lysine with the help of methionine. It
up clot formation. Several substances as
esis, increased thrombosis from increase
improves triglyceride levels, total choles-
shown Table 3 can be helpful. Coenzyme
in plaminogen activator/inhibitor, and
terol and increases HDL. The n-3-polyun-
Q10 for example, can inhibit the Lpa
decreases through a hepatic mechanism,
saturated acids in large enough doses
receptor expression.
which will decrease HDL while increasing
have been shown to be helpful in many
Table 4 – Homocysteine Reduction
studies. The DART study and most recent-
ly the GISSI study (published in The
Lancet) are good examples. The role of
Folate (folic acid) . . . . . . . . . . . .800 mcg-5 mg/day
omega-3 fatty acids are several, but
TMG (trimethylglycine) . . . . . . . . . . 250-1000 mg/day
recent studies report that their most pro-
found effects may be on arrhythmogene-
Also helpful are: Serine, Glycine, and NAC (n-acetyl cysteine)
sis as well as inflammation. The GISSI
study reported a substantial decrease in
triglyceride production. One of the most
cardiovascular events as a result of fish
There are many published studies
devastating effects is the glycosylation
oil supplementation. I believe the study
supporting homocysteine as a risk factor
process, whereby circulating glucose
results, although impressive, would have
for vascular disease. Homocysteine has
attaches to proteins. Eventually this leads
been even more dramatic had the investi-
also been considered a good marker for
continued on page 5
8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:44 AM Page 4
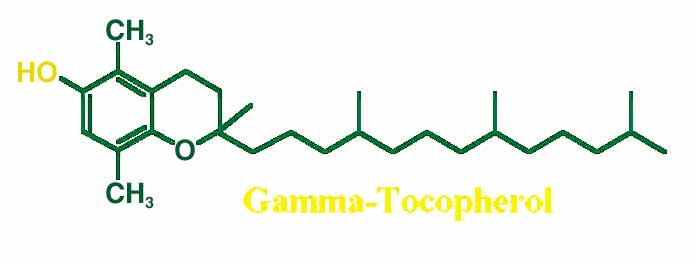
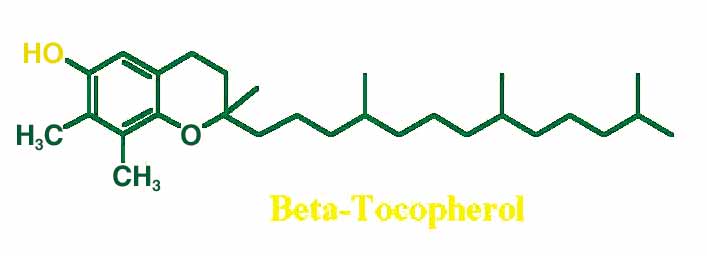
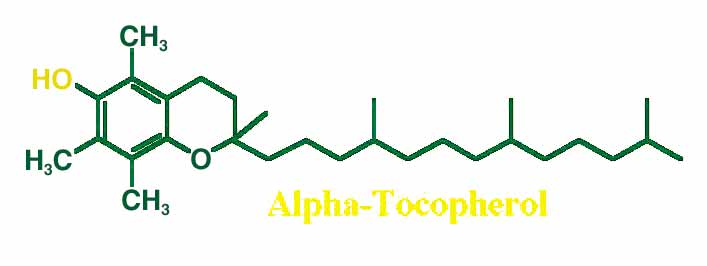
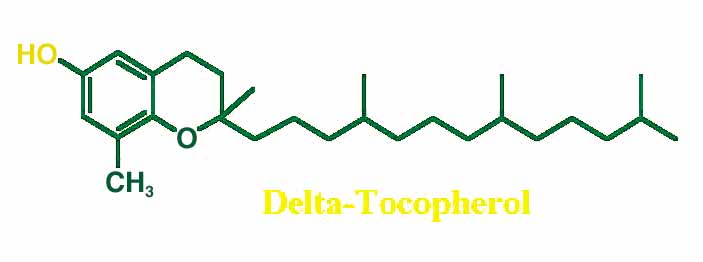
GAMMA-TOCOPHEROL: ITS IMPORTANCE AND UNIQUE PROPERTIES
When the term "vitamin E" is used, alpha-tocopherol is
Alpha-tocopherol is generally thought of as the most pow-
generally what comes to mind. However, vitamin E is actually
erful antioxidant of the various tocopherols, and due to its
a collective term that encompasses 3 other tocopherols (beta,
structure it can more readily donate electrons compared with
gamma, and delta) in addition to alpha-tocopherol. These
gamma-tocopherol. Gamma-tocopherol, however, can better
molecules are differentiated by the number and placement of
quench certain dangerous reactive nitrogen species such as
methyl groups on their structure (see figure). Recent research
peroxynitrate and nitrogen dioxide, both of which have been
has been revealing that gamma-tocopherol possesses some
associated with a number of degenerative diseases. In fact, in
unique properties that allow it to function independently from
relation to alpha-tocopherol it has been reported that gamma-
as well as synergistically with alpha-tocopherol.
tocopherol is superior in detoxifying nitrogen dioxide to lessharmful compounds. In addition to its antioxidant properties,
Alpha-tocopherol is the major form of vitamin E that
gamma-tocopherol has also been shown to possess anti-
can be found in blood as well as many tissues in humans. Due
inflammatory properties and can inhibit the activity of
to its abundance in the body research has generally focused
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and production of prostaglandin
on alpha-tocopherol, with less emphasis on the other isomers.
E2. Given the role that inflammation plays in the pathology of
However, gamma-tocopherol is the major form of vitamin E
cardiovascular disease this finding is particularly important.
consumed in the diet and is found in many plant seeds and the
Some researchers have also reported that gamma but not
oils made from them. It has been estimated that gamma-
alpha-tocopherol levels are lower in those with cardiovascular
tocopherol represents 70% of the vitamin E consumed in the
disease compared with control subjects. Recent work has also
typical US diet. Once in the body, the metabolism of alpha
brought to light a relationship between gamma-tocopherol
and gamma-tocopherol differs signifi-
and prostate cancer. In a case-control study, the
cantly. Alpha and gamma-tocopherol are
correlation between alpha-tocopherol, gamma-
absorbed similarly from the gastrointestinal
tocopherol, selenium intake and prostate cancer
tract and secreted into chylomicron
was examined. The researchers found a signifi-
particles without selective discrimination.
cant inverse correlation between the intake of
However, when the chylomicron remnant
gamma-tocopherol and the incidence of
particles are taken up by the liver, alpha-
prostate cancer (i.e., the greater the intake of
tocopherol is preferentially incorporated
gamma-tocopherol, the lower the risk of dis-
into very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)
ease). Most intriguing was that alpha-toco-
cholesterol particles. This preferential
pherol and selenium intake was only protective
placement of alpha compared with
when gamma-tocopherol intake was also high.
gamma-tocopherol into VLDL particles is aresult of the presence of a protein in the
These interesting scientific findings, coupled
liver called alpha-tocopherol transfer pro-
with the fact that gamma-tocopherol, but not
tein. This protein is able to recognize the
alpha-tocopherol levels have been shown to
stereochemistry of the various tocopherols and has the great-
decline with age in humans give further credibility to the
est affinity for the d-alpha form. Consequently, alpha-toco-
importance of supplementing with a well-rounded mixed toco-
pherol becomes selectively located in VLDL particles, which
pherol supplement that contains significant amounts of
after circulation and metabolism are transformed in to low-
gamma-tocopherol.
density lipoprotein (LDL) particles. An interesting note is that
Helzlsouer KJ., Huang HY., Alberg AJ., et al. Association between alpha-tocopherol,
supplementation with alpha-tocopherol in the absence of
gamma-tocopherol, selenium, and subsequent prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst2000;92:2018-2023.
gamma-tocopherol leads to a reduction of both tissue and
Jiang Q., Christen S., Shigenaga MK., Ames BN. γ-Tocopherol, the major form of
plasma levels of gamma-tocopherol. Nonetheless, given its
vitamin E in the US diet, deserves more attention. Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74:714-722.
presence in chylomicrons, and presence in other lipopro-
Jiang Q., Elson-Schwab I., Courtemanche C., Ames BN. γ-Tocopherol and its majormetabolite, in contrast to αtocopherol, inhibit cyclooxygenase activity in macrophages
tein particles (albeit it at levels less than alpha-tocopherol)
and epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2000;97:11494-11499.
gamma-tocopherol does reach the circulation and plays an
McLaughlin PJ., Weihrauch JL., Vitamin E content of foods. J Am Diet Association
important role.
8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:44 AM Page 5
dioprotective property. Some have
Table 5 – Insulin Resistance Reduction
claimed that bromelain can not be effec-
tive orally, but this has since been refuted.
Researchers report that soluble fibers
(higher doses often used for short periods of time)
have a positive effect on hypertension as
well as serum-fasting insulin. Patients
C.L.A. (conjugated linoleic acid) . . . . . . . 1-3 gm/dayEFAs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3 gm/day
should be regularly tested for glycosylat-
ed hemoglobin, fasting blood sugar and
fasting insulin levels.
to advanced glycosylation end products
apy. Grapeseed extract alone has been
Inflammation and Infection
(AGE), which can be a precursor to
shown to reduce plaque size. Since most
microvascular disease. The abnormal
diets have poor consumption of antioxi-
Presently, most recognize that there
glucose/insulin metabolism augments
dants and flavanoids, supplementation
are several infectious agents that are
formation of free radicals. Of course,
with larger doses than usual for coronary
associated with coronary vascular dis-
oxidative stress is often responsible for
artery disease (C.A.D.) patients may ease. Human herpes virus 6, nanobacte-
many of the factors contributing to coro-
ria, chlamydia and cytomegalo virus all
nary artery disease. Other than the sub-
have been implicated as part of the epi-
Bromelain has been shown to have
stances noted in Table 5, caloric restric-
genesis of heart disease. Studies have
numerous therapeutic benefits, including
tion is an excellent way to decrease free
even shown 89% of patients have
effects on cytokines such as TNF-alpha,
radical formation and improve insulin
chlamydia in their hearts at the time of
IL-1beta, IL-6 and IL-8. Studies also give
sensitivity. Equally as important is a reg-
bypass surgery. Most investigators agree
evidence that bromelain may inhibit
ular exercise program given that insulin
that, although these infectious organisms
platelet aggregation, an important car-
receptors are located within muscle tissue.
may not be the primary cause of heart
In addition, repletion with antioxidants is
Table 6 – Antioxidants & Biological Enzymes
also imperative (see Table 6).
AntioxidantsVitamin A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5000-10000 I.U./day
Antioxidants and Biological Enzymes
Vitamin C (buffered preferred) . . . . . . .1000-4000 mg/day
There are many studies that support
Vitamin E (unesterified, natural alpha-tocopherol
with mixed tocopherols and tocotrienols) . . . 800-1600 I.U./day
the importance of adequate antioxidant
Selenium . . . . . . . . . . . . . .200-1000 mcg/day
levels and the occurrence of coronary
artery disease. In several instances, it has
SOD (superoxide dismutase) . . . . . . . 2000-3000 MF/units
been postulated that antioxidant use is
Catalase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2000-3000 MF/units
more important than the control of lipid
Table 7 – Inflammation and Infection
levels. It is well known that cholesterol in
Bromelain (acid stable) . . . . . . . . . .500-2000 mg/day
itself is not problematic, but the exposure
of cholesterol to the oxidation process cer-
tainly can generate plaque. Grapeseed
Central fatty acids (EFAs) . . . . . . . . . 5000-10000 mg/day
extract, vitamin E and vitamin C are
Curcuma longa . . . . . . . . . . . . .200-1200 mg/day
important components of antioxidant ther-
Vitamin C (buffered) . . . . . . . . . . .1000-4000 mg/day
8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:44 AM Page 6
disease, they significantly contribute to a
sequent increase in epinephrine/norepi-
seems to reduce the heart failure associ-
hypercoagulable state. The use of low-
nephrine. Also, melatonin levels could
ated with low coenzyme Q10. Another
dose broad-spectrum antibiotics such as
possibly explain why the majority of
study on the usefulness on coenzyme
tetracycline has been suggested along
heart attacks occur in the early morning
Q10 in clinical cardiology demonstrated
with aggressive enzyme usage. It seems
hours. Melatonin has also been found to
large doses over time will reduce overall
that this combination affords the best
inhibit platelet aggregation. Saliva mela-
cardiac medication requirements signifi-
result of reducing infection and inflam-
tonin sampling can be obtained from sev-
cantly. (See insert on this page "Co-
mation. Several studies have shown the
eral laboratories throughout the country.
enzyme Q10) Taurine, an amino acid
overall effectiveness of enzyme use is
has likewise been shown to have positive
Table 9 depicts several substances
greater than the non-steroidal anti-
cardiac effects and diuretic properties.
with either ionotropic (increase heart
Hawthorne berry has been used for
years by western herbologists as a good
Table 8 – Sympathetic Tone
ionotropic natural agent.
contractibility) or chronotropic (rhythm
The sympathetic nervous system
heart stabilizing) effects on the heart.
A multiangle assertive approach
(flight or fight) plays an important role in
Regular use of these substances can often
seems to be appropriate when treating
C.A.D. Greater than usual sympathetic
augment typical conventional medica-
the coronary artery disease patient.
tone will increase heart rate and elevate
tions of similar nature, i.e., digitalis and
Hormonal issues should also be exam-
blood pressure. Increased sympathetic
antiarrythmics. Several studies have
ined and a saliva profile may prove effi-
activity has often been demonstrated in
shown magnesium to be an excellent pre-
cacious in determining DHEA, estrogen,
patients with C.A.D. Increased levels of
ventative of dysrythmias and can be
progesterone, and testosterone levels.
adrenal medulla hormones, i.e., norepi-
especially useful in intravenous doses of
Recently, much has been written about
nephrine and epinephrine damage the
2-3 gm in the early stages of heart attack
hormones and their inverse relationship
arterial lining, increase platelet aggrega-
and for several days thereafter. Its use
with coronary artery disease. By routine-
tion and increase oxidized cholesterol,
can prevent the serious rhythm distur-
ly screening with these saliva and blood
all which lead to a faster generation of
bances that often accompany myocardial
tests, you will be able to note lipid levels,
arthrogenesis. Remember, calcium stimu-
infarction. Long-term use is also suggest-
coagulability, glucose/insulin levels,
lates sympathetic discharge, whereas,
ed since most patients are magnesium
melatonin level, hormone levels, inflam-
magnesium has antagonistic properties.
deficient. Other studies have determined
matory status, and homocysteine levels.
Therefore, appropriate levels of magne-
that the use of coenzyme Q10 in dosages
A practitioner could then choose, from
sium and melatonin help to control an
of 300 mg/day one week prior to car-
the tables provided, those nutritional sup-
imbalanced sympathetic nervous system.
diac surgery improves three-fold the
plements that would address areas of
serum levels and tissue levels in the heart
concern revealed by the test results.
Researchers have demonstrated that
of this nutraceutical. This improvement
patients with C.A.D. have nighttime
Table 9 – Ionotropic and Chronotropic Augmentation
melatonin levels that are 1/5 lower than
Magnesium . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1600-3000 mg/day
healthy controls. Explanatory physiology
is likely to be related to increased night-
Hawthorne Berry . . . . . . . . . . . . .250-500 mg/day
time sympathetic discharge and the sub-
Coenzyme Q10 . . . . . . . . . . . . .200-400 mg/day
8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:44 AM Page 7
Abnormal tests would be noted and
repeated after an appropriate length of
treatment and adjustment of the treat-
COENZYME Q10:
ment plan, by either increasing doses of
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION
already-prescribed nutraceuticals, with
or without the addition of new agents.
Coenzyme Q10, (CoQ10) also known as ubiquinone has been receiving
Further adjustment in the program would
an increasing amount of attention over the past 5 years for its cardioprotec-
be necessary when the patient is taking
concurrent medicine(s). Drugs that have
tive abilities. CoQ10 is a fat-soluble molecule synthesized from cholesterol
similar properties to those nutraceuticals,
and located predominantly in mitochondria (the cell's powerhouse) where it
that your patient is already taking, would
plays a vital role in energy production. Specifically CoQ10 is crucial for the
require appropriate adjustment. For
example, patients taking anti-coagulants
proper transfer of electrons through the mitochondrial respiratory chain.
would require lower doses of those sup-
Given that heart muscle requires a tremendous amount of energy to function
plements mentioned in Table 1. However,
properly, it is not unusual that significant levels of CoQ10 can be found in
other patients, taking lipid-lowering
drugs, may require increased doses of
heart muscle. Since CoQ10 levels have been found to be lower under cer-
CoQ10. Remember, many coronary-
tain circumstances, researchers have been investigating the effect that sup-
related medications cause other nutrition-
plemental CoQ10 can have on heart function. Not surprisingly, numerous
al deficiencies and I suggest that you
refer to a text describing drug-herbal
clinical studies have demonstrated improvements in functional parameters of
and drug-nutrient interactions.
the heart in patients with congestive heart failure after supplementation with
CoQ10. CoQ10 treatment prior to bypass procedures has also yielded
The use of EDTA, although it is con-
more positive outcomes when compared with patients who did not receive
sidered by the conventional medical
supplementation. CoQ10 levels have also been shown to be reduced in
community as controversial, has revealed
in many studies to have a significant
patients taking statin drugs, as cholesterol is required for the synthesis of
place in the treatment of coronary artery
CoQ10 in the body. CoQ10 has been shown to be an effective antioxidant,
disease along side the nutraceuticals pre-
protecting against lipid peroxidation, DNA and protein oxidation and is also
sented in this paper. Heavy metals do
play a role in artherogenesis and should
capable of functioning synergistically to help regenerate other antioxidants.
be studied further. Don't forget, in the
The research community continues to find strong data indicating the benefits
midst of this complex array of nutraceuti-
from supplementation with CoQ10, especially in the area of cardiovascular
cals, water itself may improve the out-
comes of coronary events. Simply drink-
health as it relates to congestive heart failure.
ing 4 or more glasses of pure water each
day, can decrease myocardial infarction
by more than 50%.
8537-layout mar25.qxd 3/26/02 10:44 AM Page 8
Arsenio, L., et al. Effectiveness of Long-Term Treatment with Pantethine
Langsjoen, H., et al. Usefulness of Coenzyme-Q-10 in Clinical
in Patients with Dyslipidemias. Clin Ther, 1986; 8: 537-545.
Cardiology: A Long Term Study. Mol Aspects Med, 1994; 15 Suppl:s165-175.
Baggio, E., et al. Italian Multicenter Study on the Safety and Efficacyof Coenzyme-Q-10 as Adjunctive Therapy in Heart Failure. Co-Q-10
Lipson, S.F., Ellison, P.T. Development of Protocols for the Application
Drug Surveillance Investigators. Mol Aspects Med, 1994; 15 Suppl:
of Salivary Steroid Analysis to Field Conditions. American Journal of
Human Biology, 1989; 1:249-255.
Broughton, D.L., Taylor, R.L. Review: Deterioration of Glucose
Lukaczer, Dan. Nutritional Support for Insulin Resistance. Applied
Tolerance with Age: The Role of Insulin Resistance: Age and Aging,
Nutritional Science Reports, July 2001; pp. 1-6.
1991; 20: 221-225.
Maurer HR. Bromelain: biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use.
Brugger, P., et al. Impaired Nocturnal Secretion of Melatonin in
Cell Mol Life Sci 2001;58:1234-45.
Coronary Artery Disease. Lancet, 1995; 345: 1408.
Merghioli, Robert, et al. Dietary Supplementation with N-3
Cantin, B., et al. Lipoprotein (a) An Independent Risk Factor for
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Vitamin E After Myocardial
Ischemic Heart Disease in Men? The Quebec Cardiovascular Study. J
Infarction: Results of the GISSI-PREVENZIONE Trial. The Lancet,
Am Cardiol, 1998; 31:519-525.
Volume 234, Aug 7, 1999; pp 447-495.
Cardinali, D.P., Del Zar, M.M., Vacas, M.I. The Effects of Melatonin in
Mori, T.A., et al. Interactions Between Dietary Fat, Fish, and Fish Oils
Human Platelets. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Ther Latinoam, 1993; 43:
and their Effects on Platelet Function Men at Risk with Cardiovascular
Disease. Arterioscler Throm Vasc Biol, 1997; 17:279-286.
Chappell, L.T., Stahl, J.P. The Correlation Between EDTA Chelation
Phillips, R., Lemon, F., Kuzma, J. Coronary Heart Disease, Mortality
Therapy and Improvement in Cardiovascular Function: A Meta-
Among Seventh Day Adventists with Differing Dietary Habits. Am J
Analysis. J Adv Med, 1993; 6: 139-160.
Clin Nutr, 1978 Oct 31;(10 Suppl): 5191-5198.
Dabbs, J.M. Savory Testosterone Measurements: Collecting, Storing
Rosenfeldt, Franklin, et al. Experience with Coenzyme-Q-10 in
and Mailing Saliva Samples. Physiology and Behavior, 1991; 49:
Cardiac Surgery Patients. 2nd Conference of the International Co-Q-
10 Association. Frankfurt, Germany, December 1-3, 2000.
El-Enein Ama, et al. The Role of Nicotinic Acid and Inositol
Watson, P.S., Scalia, G.M., et al. Lack of effect of Coenzyme-Q-10
Hexanicotinate as Anti-Cholesterolemic and Anti-lipemic Agents. Nutr
on Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure.
Rep Intl, 1983; 28: 899-911.
J Am Coll Cardiol, 1999, May; 33(6):1549-1552.
Folsom, A. Homocysteine: Not a Risk Factor. Circulation 98, 1998;
Weiss, Decker. Part One: Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and
196-199, 204-210.
Fundamental Nutrition. Applied Nutritional Science Reports, Feb2000, pp. 1-6.
Fox, M. More Evidence that Infections Cause Heart Disease. ScienceNews, Sept 18, 2000.
Welsh, A.L, Edede, M. Inositol Hexanicotinate for Improved NicotinicAcid Therapy. Int Record Med, 1961; 174:9-15.
Fukagawa, N.K., Anderson, J.W., et al. High-Carbohydrate, HighFiver Diets Increase Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity in Healthy Young and
Weiss, Decker. Part Two: Cardiovascular Disease Nutrtional
Old Adults. Am J Clin Nutr, 1990; 52: 524-528.
Management of Clinical Markers. Applied Nutritional ScienceReports, Feb 2000, pp. 1-6.
Ghen, M.J., et al. The Advanced Guide to Longevity Medicine. 2001,Landrum, South Carolina, pp. 193-201, 239-246.
Graham, I.M., et al. Plasma Homocysteine as a Risk Factor forVascular Disease: The European Concerted Action Project. JAMA,1997; 277; 1775-1781.
Hancke, C., Flytlie, K. Benefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy inArteriosclerosis: A Retrospective Study of 47- Patients. Journal ofAdvancement in Medicine, 1993; 6(3); 161-172.
2002 Douglas Laboratories. All Rights Reserved.
Source: https://www.douglaslabs.ca/pdf/nutrinews/Coronary%20Artery%20Disease%20NN%20(03-02).pdf
Tender No: AIIMS/BBSR/MS/15/183 Procurement of Emergency Drugs & Disposables for AIIMS Hospital, Bhubaneswar DME Stage Start Date & Time NIT Issue Date 24/06/2015 at 11.00 AM Last Date of Submission 14/07/2015, 12.00 P.M Tender opening date 14/07/2015, 15.00 P.M
CENTRAL UNIVERSITY OF HARYANA JANT-PALI, MAHENDERGARH Notice on Measures for avoiding Dengue Fever Concerning the recent outbreak of dengue fever in and around National Capital Region Delhi, it is informed to all concerned that Dengue fever is transmitted through mosquitoes infected with the dengue virus and not through contact with infected humans. Once infected, individuals will experience mild symptoms and overall mortality rates are low. Regardless, due to possible high fever and other uncomfortable flu-like symptoms, University authorities recommend avoiding areas with high mosquito populations, using insect repellent when outdoors, and avoiding bare skin exposure as much as possible. Symptoms of dengue fever manifest in three to seven days after infection and include sudden fever, intense headaches, and pain in the joints. If you think you have been infected with the dengue virus, please consult a physician immediately. When you are outside, please make sure you take precautions and be aware of the following in order to reduce the chances of mosquito bites:










